Code Highlight Demo 01


code highlight
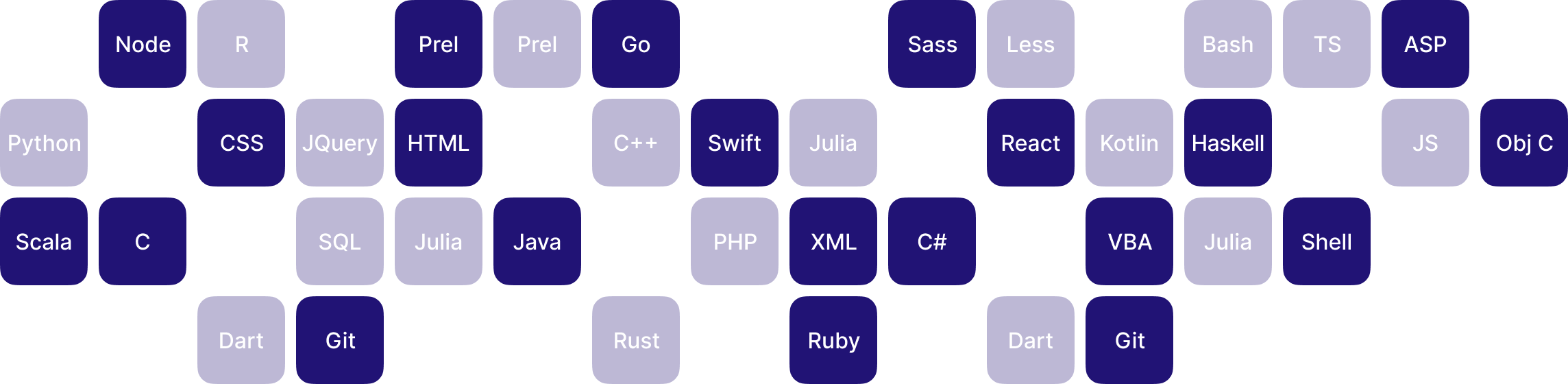
Support more 30 Langs

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.close();
int result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println("Factorial of " + number + " is " + result);
}
}
Code Highlight Demo 02
Highlighting the Benefits:
A Guide to Our Key Features
>>> type(true)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#92>", line 1, in <module>
type(true)
NameError: name 'true' is not defined
>>> type(false)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#93>", line 1, in <module>
type(false)
>>> type(true)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#92>", line 1, in <module>
type(true)
NameError: name 'true' is not defined
>>> type(false)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#93>", line 1, in <module>
type(false)
NameError: name 'false' is not defined
## Python Programming ##
>>> type(true)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#92>", line 1, in <module>
type(true)
NameError: name 'true' is not defined
>>> type(false)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#93>", line 1, in <module>
type(false)
## Python Programming ##
>>> type(true)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#92>", line 1, in <module>
type(true)
NameError: name 'true' is not defined
>>> type(false)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#93>", line 1, in <module>
type(false)
## Python Programming ##
>>> type(true)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#92>", line 1, in <module>
type(true)
NameError: name 'true' is not defined
>>> type(false)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#93>", line 1, in <module>
type(false)
Code Highlight Demo 03
Screen Artistry Meets Code Craftsmanship
import React, { useState } from "react";
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
function handleIncrement() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
function handleDecrement() {
setCount(count - 1);
}
return (
<div>
<h1>Count: {count}</h1>
<button onClick={handleIncrement}>Increment</button>
<button onClick={handleDecrement}>Decrement</button>
</div>
);
}
export default Counter;

Code Highlight Demo 04

Elevate your coding with AI assistance.
Transform your programming workflow by leveraging the power of AI and improve your coding efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
def fizz_buzz(n: int) -> None:
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if i % 3 == 0 and i % 5 == 0:
print("FizzBuzz")
elif i % 3 == 0:
print("Fizz")
elif i % 5 == 0:
print("Buzz")
else:
print(i)
fizz_buzz(15)

>>> type(true)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#92>", line 1, in <module>
type(true)
NameError: name 'true' is not defined
>>> type(false)
Code Highlight Demo 05


Python
Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language.
Introducing Python
Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. It is known for its simple, readable and easy-to-learn syntax, making it a popular choice for beginners and experienced developers alike. Python is widely used in various fields such as web development, scientific computing, data analysis, artificial intelligence and more. It has a large, active and supportive community, which has contributed to the development of numerous libraries and packages, making it easy to perform complex tasks with a few lines of code. Python’s versatility and readability make it a popular choice for many industries and organizations.
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load data from CSV file
data = pd.read_csv('sales_data.csv')
# Group data by product and sum the sales
sales_by_product = data.groupby('product')['sales'].sum()
# Create a bar chart of sales by product
plt.bar(sales_by_product.index, sales_by_product.values)
plt.title('Sales by Product')
plt.xlabel('Product')
plt.ylabel('Sales')
plt.show()
Understand Python
In this step of learning Python, the focus is on gaining a solid understanding of the basics of the language. This includes learning about the Python syntax, data types, variables, and operators. You will also learn how to write your first Python program, use print statements to display output, and make basic calculations.
The goal of this step is to lay the foundation for further learning and to give you a sense of how Python works. You will gain an understanding of the basic structure of a Python program, how to store and manipulate data, and how to perform basic operations.


